The Vice President of Nigeria, Prof. Yemi Osinbajo, this week at an interactive session on “Stabilizing The Mediterranean” at the World Economic Forum in Davos, Switzerland, said Africa still has the high potential to become the next factory of the world. Osinbajo said with rising labour wages in China and the deepening of right economic conditions in several Africa countries, there were strong signs of Africa becoming the skill and production hub for the world. Below are excerpts of remarks at the interactive session.
Q: How realistic is Africa replacing China as the factory of the world, how realistic is that? How do you look at the Marshall plan for Africa, is it something you think is credible?
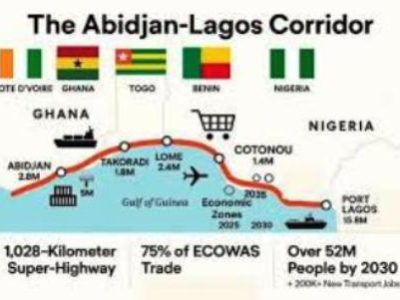
Vice President: Let me begin with the Africa Rising narrative and all of the possibilities around Africa replacing China as the factory of the world. I think that probably is in the natural cause of things. Even now, we see that as wage costs go up in China, Africa is becoming the obvious choice for some certain industries, so it is clear that will happen and there are quite a few initiatives in that direction already; there are a few countries like Ivory Coast, Nigeria, with the development of Special Economic Zones, with partnerships coming from China.
I think those sorts of arrangements will very quickly absorb labour because obviously, you are looking at growing populations in Africa, the projections as you know are in the next 20 years or so, we are looking at the youth population… probably 70% of Africa’s population would be young people and Africa would probably about be the third largest population.
I think that the critical thing is to see that we cannot deal with this in any quick way, there are no quick fixes to this, we have got to look at this long term, because clearly there’s no way that African economies will ramp off quickly enough to be able to meet all of the expectations, especially all of the projections around population. So this is going to be a long walk and I think that it is important for all of us to see this as such.
The idea of the Marshall Plan is to me, in some sense, bringing old solutions to what really is a dynamic problem. I think that what Africa needs and what a lot of the southern neighbours of the Europeans need are fairer trade policies and a cocktail of policies that centre on job creation in those locations, more investments, but I think more thinking through those ideas and policies that creates more opportunities, partnership between Europe and Africa.
I don’t think that aid has worked through the years. I think that there’s a need for possibly just much more commitment to the whole process. I mean there have been multi-processes, several of them, but I certainly think that if we look at this as a major global problem and when you look around and look at extremism, terrorism and all of the various things that are exported along with illegal migration, it is a global problem and we really does deserve a global solution and the way to look at that is by coming together to reason these things through, but frankly it is not by those Marshal Plans off the shelf, I think it is more nuanced than that.
Q: Do you feel that values of human rights are being compromised in order for Europe to have tactical immediate solutions?
Vice President: I certainly agree that it was a great shock to see actual slave dealings in this century; it was absolutely horrifying to see that. What we are seeing is a degeneration of criminal activities where you find that state capacity is unable to maintain international human rights norms.
One of the crucial things is to encourage repatriation. Nigerian government for example is working with the Libyan government in repatriating everyone who is in the camps. It is a slow process because there are those who claim nationalities because they see a way out of the camps. There is also a great deal of willingness on the part of those who are in the camps to go back because it is entirely voluntary. There is pressure where there is no state capacity or inadequate state capacity to maintain law and order and international human rights norms. The pressure is a bit too much for the Libyan authorities, so what you find is that the criminal gangs and all of these asymmetric type organizations dominate the space and we may not be able to do much without relieving the Libyan authorities of a lot of the illegal migrants in their custody or their country.
Q: With a Yes or No, 5 years from now, are we still going to be seating here having the same discussion?
Vice President: Would you give us a chance to say, “I hope not?” (Laughter). I really suspect yes.