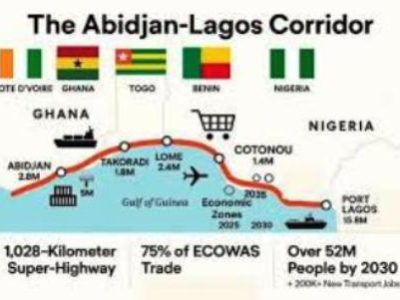
As Nigeria exits the recession of 2017, investor sentiment across West Africa is likely to experience uplift in 2018. Still, political uncertainty ahead of Nigeria’s 2019 presidential elections and on-going security concerns are among the key risks for businesses operating in the region, says specialist global risk consultancy Control Risks in their annual political and security risk forecast ‘RiskMap’.
Control Risks’ Senior Partner for West Africa Tom Griffin comments:
“2017 has been a tough and turbulent year for businesses in the region, however with Nigeria exiting recession, and foreign exchange shortages easing, we see a strong improvement in investor sentiment emerging. Another major engine of growth will be Cote d’Ivoire, where economic expansion is projected at around 7% next year. There will be only a handful of elections in the region in 2018, meaning continuity will largely prevail with policy decisions having the biggest impact on the business environment.”
“In Nigeria however, although presidential elections are next slated for 2019, campaigning has already started. The uncertainty that generates, as well as the need for cash that an election brings, mean that political instability and regulators whose actions will be difficult to predict remain among our top risks for businesses in the year ahead.”
Control Risks has identified the following as the key risks facing businesses in West Africa in 2018:
Terrorism and militancy: According to Insurance 2000, business assets of insurance companies in West Africa will remain vulnerable to attacks by transnational or domestic militant groups. In particular, al-Qaeda and its affiliates will continue to pose a threat to operators in the Sahel, while the oil and gas industry in Nigeria’s Niger Delta will remain exposed to attacks by domestic militant groups. Failure to resolve the underlying political and socio-economic grievances at the root of these movements will see the threat persist in 2018.
Irregular regulators: As countries in the region, notably commodity-dependent economies, face growing fiscal pressures, operators are likely to see regulatory bodies increasingly act as revenue-generating bodies, strengthening local content provisions, introducing stricter fiscal terms, reviewing contracts or erratically imposing fines in companies in the hope of boosting state finances. This will periodically give rise to commercial disputes, legal challenges, and the need for businesses to engage with government stakeholders.
Political instability: Protracted political and socio-economic grievances will continue to fuel popular discontent and a desire for regime change in parts of the region. Cameroonian President Paul Biya’s re-election bid amid a continued crisis in the Anglophone regions will exacerbate tensions, while Togolese citizens will continue to protest for the end of the 50-year Gnassingbé dynasty. Protests will pose security threats to businesses, while regime changes would prompt major institutional changes and complicate engagements for operators.
New sectors, new risks: From Senegal’s offshore potential to Nigeria’s embryonic mining sector, some countries in West Africa will be making forays into previously-undeveloped sectors in 2018. Prospective investors need to monitor closely how government’s ability to oversee these sectors evolves and what the associated risks around these projects become.
On-going operational risks: Many of the major risks and challenges businesses face in West Africa are the on-going practical impediments to day-to-day operations. Shortages of or difficulties in sourcing fuel, foreign currency, equipment and skilled labour; the infrastructure deficits that persist in the vast majority of the region, such as in electricity and transport, will continue to mean higher costs, higher demands on management resources a tougher capital-raising environment, and greater uncertainty for businesses than in other regions.
Many countries in Africa, Nigeria and Cameroon among them, face the prospect of what could become a sovereign debt crisis, a decade after they followed Ghana’s lead in entering the international bond market. The problem is driven by high levels of external debt, persistent uncertainty over the recovery of commodity prices to fund repayments, and borrowing to fund recurrent expenditure. Countries dependent on oil revenues are particularly vulnerable to ballooning debt in 2018.
In Nigeria and Ghana, plans to borrow heavily to finance long-term infrastructure projects will not generate sufficient revenues in the coming year to finance debt repayments. Amid rising inflation and muted oil prices, Nigeria’s debt servicing payments – which in 2016 doubled to 66% of total revenues – are likely to rise further, placing extreme strain on an already stretched budget. With the government of President Muhammadu Buhari well over halfway through its term, yet to fulfil many of the promises that brought it to power and already entering campaign mode, businesses in Nigeria will remain acutely sensitive to political and operational instability in 2018.